Odoo's architecture is designed for extensibility, allowing developers to customize existing functionalities without altering the core code. This is primarily achieved through inheritance, a powerful mechanism that enables you to modify or extend standard Odoo views, menus, and actions. By leveraging inheritance, you can tailor Odoo to specific business needs, add new features, or adjust the user interface, all while ensuring your customizations are robust and compatible with future Odoo upgrades.
This guide will walk you through the technical process of inheriting views, menus, and actions in Odoo 19, providing practical examples for each scenario.
1. How to Inherit Odoo Views
View inheritance is the most frequent method for customizing Odoo's user interface. It allows you to modify existing form, tree (list), search, or kanban views by adding new elements, changing attributes of existing ones, or even removing them. The core components for view inheritance are the inherit_id attribute and xpath expressions.
To inherit a view, you define a new XML record with a unique id, specify ir.ui.view as the model, and set the inherit_id to the external ID of the original view you want to modify. Within the <field name="arch" type="xml"> tag, xpath expressions are used to precisely target elements inside the inherited view.
Example 1: Adding a New Field to an Existing Form View
Let's demonstrate by adding a new x_internal_notes field to the standard res.partner (Contacts) form view.
Step 1: Define the Custom Field in Python
First, create your custom field in a Python model that inherits res.partner. For instance, in my_module/models/res_partner.py:
from odoo import fields, models
class ResPartner(models.Model):
_inherit = 'res.partner' # Inherit the existing res.partner model
x_internal_notes = fields.Text(string="Internal Notes")
Step 2: Inherit the View in XML
Next, create an XML file (e.g., my_module/views/res_partner_views_inherit.xml) to inherit the res.partner form view and integrate your new field:
<odoo>
<data>
<record id="view_partner_form_inherit_my_module" model="ir.ui.view">
<field name="name">res.partner.form.inherit.my.module</field>
<field name="model">res.partner</field>
<field name="inherit_id" ref="base.view_partner_form"/>
<field name="arch" type="xml">
<!-- Use xpath to locate where to add the new field -->
<xpath expr="//field[@name='website']" position="after">
<field name="x_internal_notes"/>
</xpath>
</field>
</record>
</data>
</odoo>
- inherit_id="base.view_partner_form": This attribute points to the external ID of the original Contacts form view.
- <xpath expr="//field[@name='website']" position="after">: This xpath expression precisely targets the field named 'website'. The position="after" attribute instructs Odoo to insert our new x_internal_notes field immediately after the 'website' field. Other common position values include before, inside, replace, and attributes.
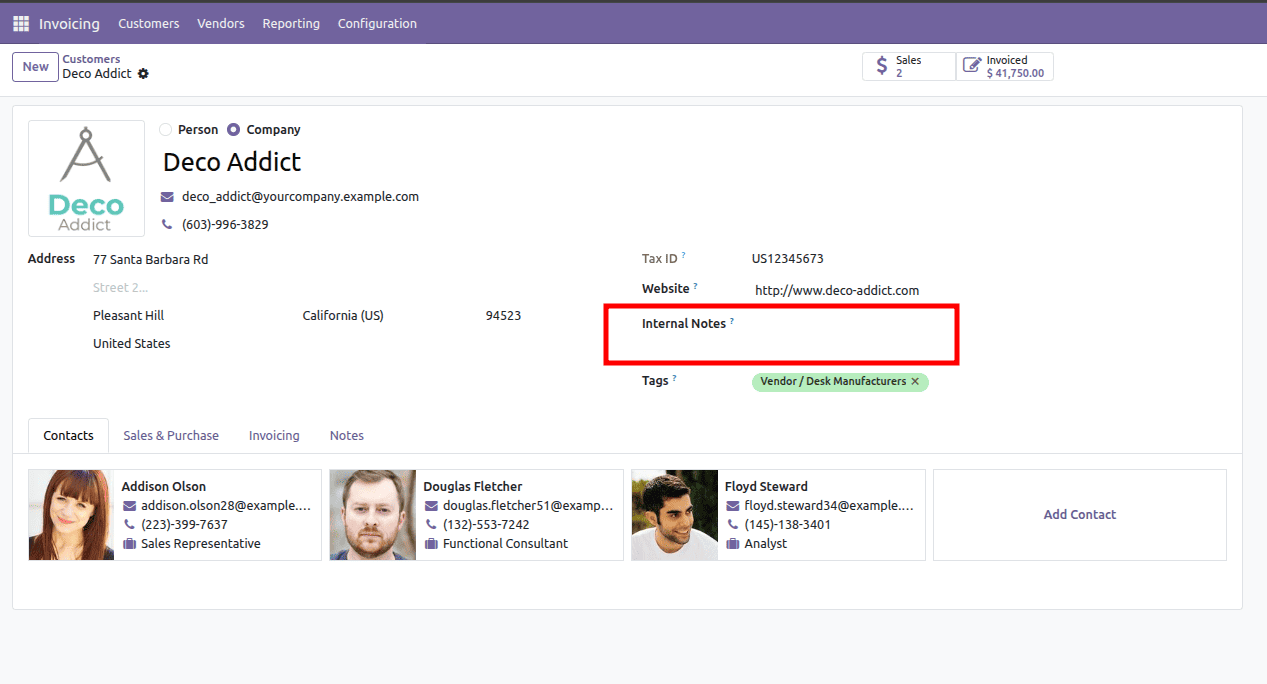
Example 2: Modifying an Existing Field's Attributes
You can also alter the attributes of existing fields, such as making a field read-only or invisible. Let's modify the vat (Tax ID) field in the res.partner form view to be read-only.
<odoo>
<data>
<record id="view_partner_form_inherit_vat_readonly" model="ir.ui.view">
<field name="name">res.partner.form.inherit.vat.readonly</field>
<field name="model">res.partner</field>
<field name="inherit_id" ref="base.view_partner_form"/>
<field name="arch" type="xml">
<xpath expr="//field[@name='vat']" position="attributes">
<attribute name="readonly">1</attribute>
</xpath>
</field>
</record>
</data>
</odoo>
- position="attributes": This position is specifically used when you want to modify the attributes of the targeted XML element.
- <attribute name="readonly">1</attribute>: This line adds or updates the readonly attribute of the vat field, setting its value to 1 (true), making the field non-editable.
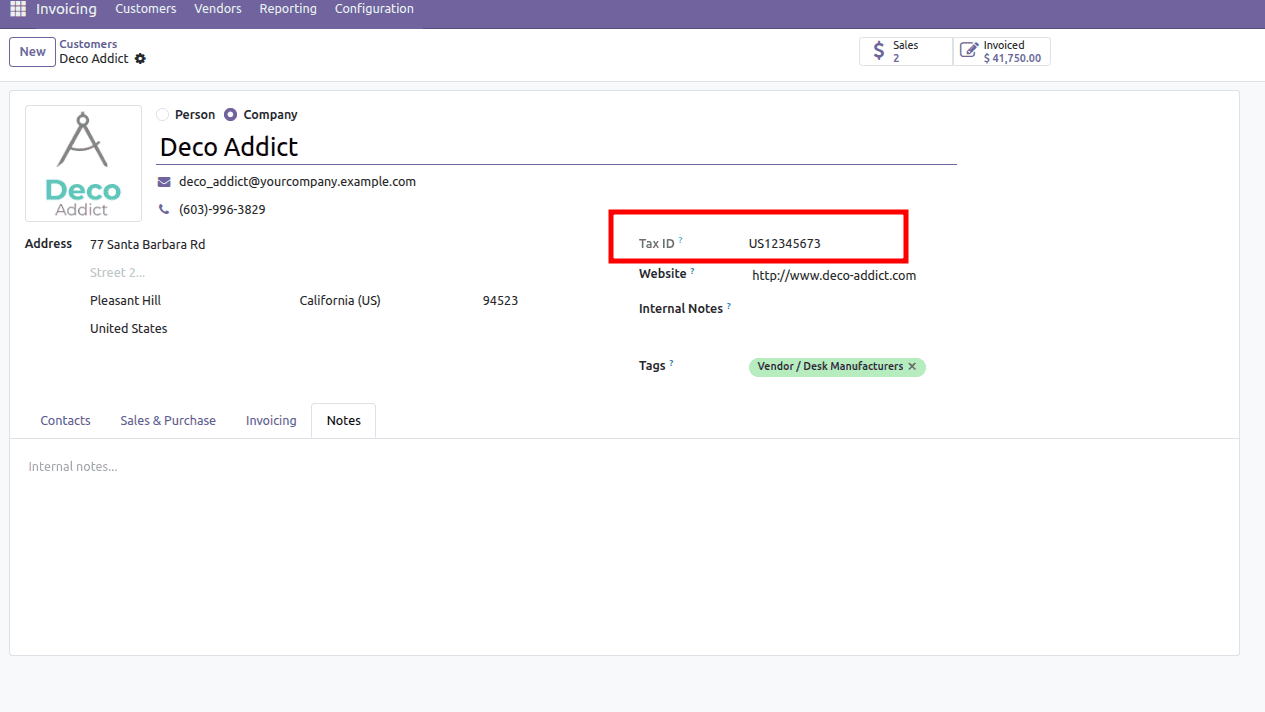
2. How to Inherit Odoo Menus (and Change Menu Name)
Menu inheritance allows you to modify existing menu items, such as changing their display labels, re-parenting them under a different menu, or adding new child menu items. This is achieved by creating a record that targets the ir.ui.menu model.
Example 1: Changing a Menu Item's Name
Let's change the name of the main "Sales" menu item to "Customer Orders". The external ID for the root Sales menu is typically sale.menu_sale_root.
<odoo>
<data>
<record id="sale.sale_menu_root" model="ir.ui.menu">
<field name="name">Customer Orders</field>
</record>
</data>
</odoo>
- id="sale.menu_sale_root": By using the exact external ID of the original menu item, Odoo recognizes that we are inheriting and modifying its properties.
- <field name="name">Customer Orders</field>: This directly updates the name field of the ir.ui.menu record, changing the text displayed for the menu item in the Odoo interface.
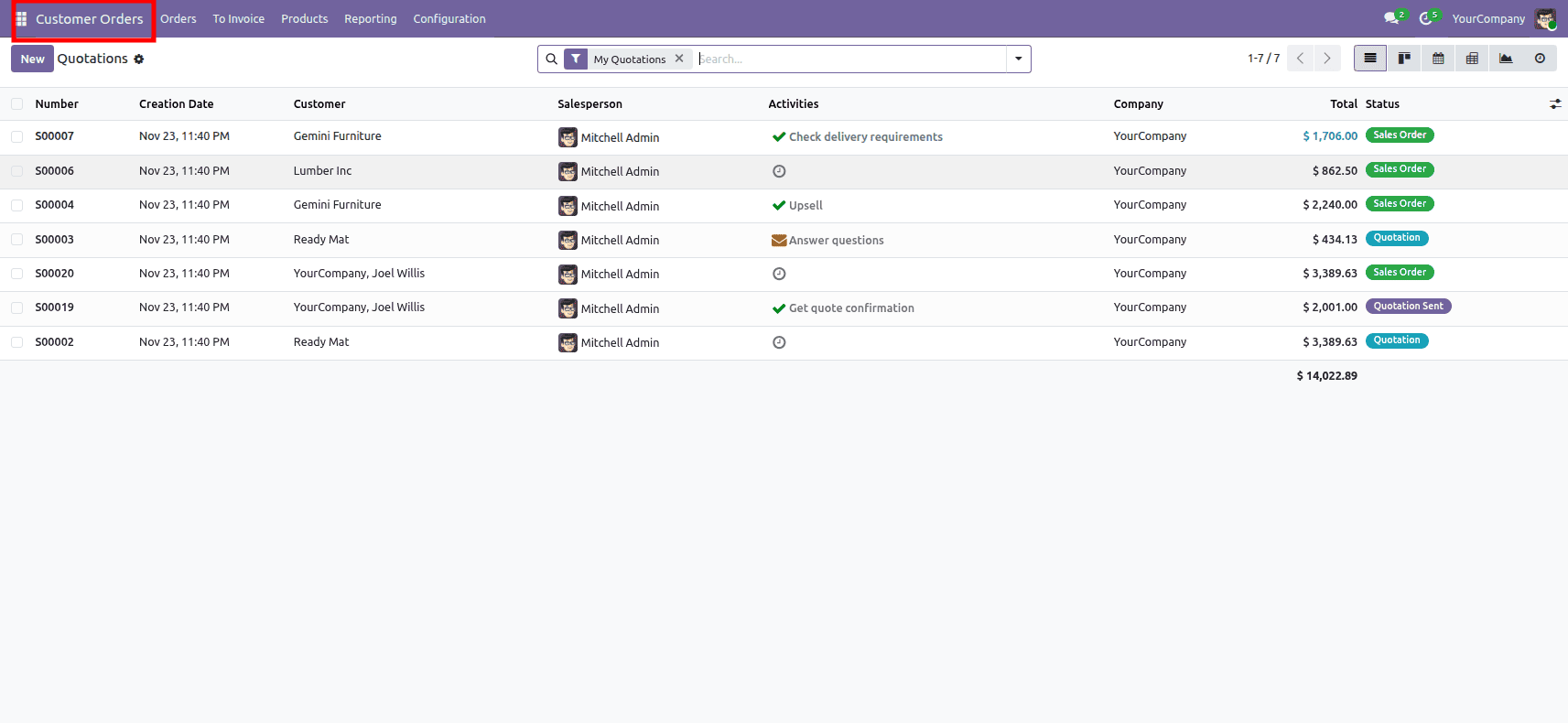
Example 2: Re-parenting a Menu Item
Suppose you want to move the "Products" menu item (which is typically found under Sales > Products) to be a direct child of the main "Sales" menu. The external ID for the "Products" menu under Sales is sale.menu_product_template_action.
<odoo>
<data>
<record id="sale.menu_product_template_action" model="ir.ui.menu">
<field name="parent_id" ref="sale.sale_menu_root"/>
</record>
</data>
</odoo>
- <field name="parent_id" ref="sale.sale_menu_root"/>: This line changes the parent_id of the "Products" menu to sale.sale_menu_root, effectively making it a direct sub-menu of the main Sales menu.
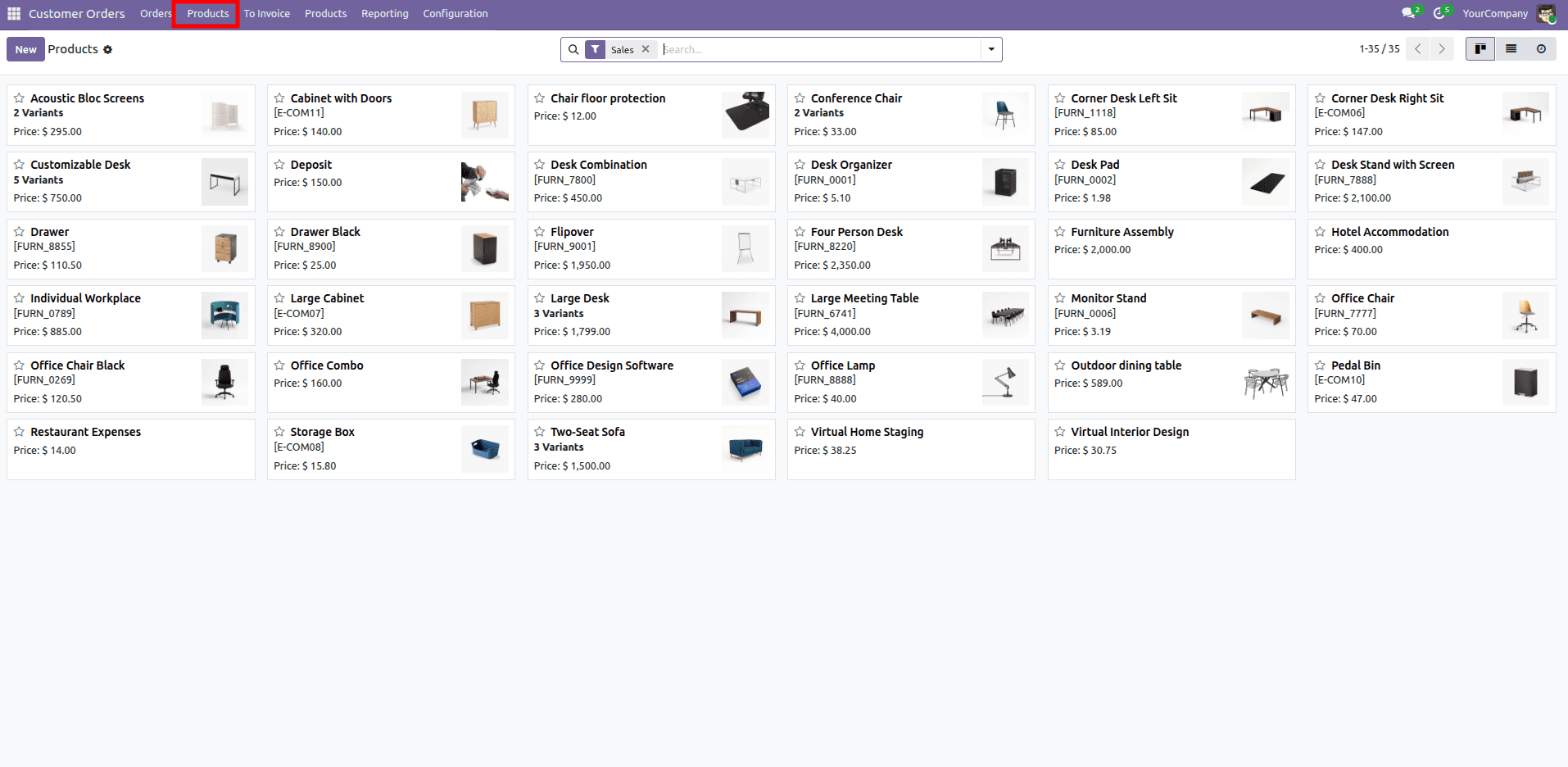
3. How to Inherit Odoo Actions
Actions in Odoo, particularly window actions (ir.actions.act_window), dictate how a view is presented. They define properties such as the target model, available view types (e.g., tree, form, kanban), default filters, and context. Inheriting actions allows you to modify these properties, thereby altering the default behavior when an action is triggered (e.g., by clicking a menu item).
Example: Changing the Default Domain and Context of an Existing Action
Let's modify the default "Customers" action to display only customers from a specific country, for instance, "India", and also set a default country when creating new contacts via this action. The external ID for the "Customers" action is typically base.action_partner_form.
<odoo>
<data>
<record id="base.action_partner_form" model="ir.actions.act_window">
<field name="domain">[('country_id.code', '=', 'IN')]</field>
<field name="context">{'default_country_id': ref('base.in')}</field>
</record>
</data>
</odoo>
- id="base.action_partner_form": We target the existing "Customers" window action using its external ID.
- <field name="domain">[('country_id.code', '=', 'IN')]</field>: This sets a default domain. When the "Customers" menu is clicked, only partner records where the country_id's code is 'IN' (India) will be displayed.
- <field name="context">{'default_country_id': ref('base.in')}</field>: This sets a default context. When a new contact is created through this action, the country_id field will automatically be pre-filled with India. ref('base.in') is used to reference the external ID of India's country record.
Important Note: For all these inheritance examples, ensure that the XML files are correctly included in your custom module's __manifest__.py file under the data key. After making changes, remember to upgrade your module for the modifications to take effect.
To read more aboutHow To Inherit Existing Pivot View Report in Odoo 19, refer to our blog, How To Inherit Existing Pivot View Report in Odoo 19.