Odoo 19 is a robust and adaptable platform for managing and personalizing a wide range of corporate applications. It is made to make it simple for developers to design solutions that meet certain requirements, such as managing data, automating processes, or developing unique workflows. Odoo 19's web controller framework, which enables developers to create unique front-end views and manage HTTP requests, is one of its most notable features. In order to enable real-time data integration and management, these web controllers are crucial for linking Odoo's backend with third-party applications or unique webpages. Businesses can expand Odoo's capabilities beyond the typical ERP configuration by utilizing web controllers to create responsive, interactive experiences for partners, suppliers, and customers.
Controllers serve as a link between the website and the back-end modules in Odoo by managing and configuring the front-end modules. Designing a smooth, dynamic website experience is made easier with controllers, which allow you to set up unique URLs that link your web pages to backend functions.
You must first establish a controllers folder in your custom module before you can begin using controllers. The required Python files and a __init__.py file should be placed inside this folder.
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from . import controllers
This new controllers folder will show up in the module structure after it is created, offering a specific area for configuring unique routes and expanding Odoo's website features.
Create a Controller File:
You can acquire backend data and present it on the front end by creating a controller in Odoo, which gives you the freedom to create unique web routes. Import the required modules and define your controller class in the controller file. We'll build a controller in this example to show every piece of sales order information.
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from odoo import http
from odoo.http import request
class SaleOrderController(http.Controller):
@http.route(['/saleorders'], type="http", auth="user", website=True)
def display_sale_orders(self, **kwargs):
sale_orders = request.env['sale.order'].sudo().search(
[], order="date_order desc"
)
return request.render(
"custom_module_name.sale_order_website_custom_layout",
{
'orders': sale_orders
}
)
When defining a URL route in Odoo, the @http.route decorator is essential. It indicates the location of a particular controller function. This is a thorough explanation of the syntax:
@http.route(['/saleorders'], type="http", auth="user", website=True)
Every element has a distinct function:
'/saleorders': The URL path is specified in this section. Odoo runs the related function beneath this decorator to create and show the relevant webpage when a user navigates to this URL (for example, <your_domain>/saleorders').
type='http': The route is meant for HTTP requests, according to this option. This indicates that browser access is intended for the route. As an alternative, JSON is utilized for API endpoints that provide JSON-formatted data.
auth='user': The degree of authentication needed to access the route is determined by this parameter. The primary choices consist of:
- 'public': Anyone, even those who are not logged in, can visit the page.
- 'user': The page is only accessible by authenticated users, or those who are logged in.
- 'bearer': Basic authentication transmits credentials and uses an API token to verify users. The Bearer uses a token for access.
- 'none': There is no need for verification, making the route fully accessible.
website: This option shows whether the controller is connected to the website, with a value of True for linked pages and False for non-website functionality.
methods: If you don't indicate which HTTP methods are allowed, then all methods are. The primary techniques consist of:
- ['GET']: used to retrieve info without altering it.
- ['POST']: used to make modifications or submit data.
sitemap: This parameter makes it possible to create sitemap links that serve as a directory for accessible sites and highlight website navigation.
cors: Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) makes it easier for servers and browsers to exchange data and make safe requests.
multilang: Frontend translations are made possible by this functionality, which enables the inclusion of multiple languages on the website.
csrf: By creating a distinct token, Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) security secures user sessions.
At the moment, the sale_orders variable contains all of the sale order information. Request.env is used in controllers to access the Odoo environment, whereas self.env is usually used in models for database interactions.
Before doing any operations, such as search or create, we use the sudo() method to handle any possible access permissions issues when working with records. This guarantees that we won't encounter permission issues when retrieving or modifying records.
Using the following code, we can now produce a webpage to show the sale order details:
return request.render(
"custom_module_name.sale_order_website_custom_layout",
{
'orders': sale_orders
}
)
The request.redirect method can be used if we need to reroute the user to a new URL rather than display a page. For instance, we would write this instead if we wanted to direct the user to /shop:
return request.redirect(‘/shop’)
Creating the View:
We may now create the sale_order_website_custom_layout XML template in the module's views folder. Since our controller has previously made reference to this view, this is required.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<odoo>
<template id="sale_order_website_custom_layout" name="Sale Orders Custom Layout">
<t t-call="website.layout">
<div class="container mt-4">
<h3>Sale Orders</h3>
<table class="table table-bordered table-striped mt-3">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Order</th>
<th>Date</th>
<th>Customer</th>
<th>Status</th>
<th class="text-end">Untaxed</th>
<th class="text-end">Tax</th>
<th class="text-end">Total</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<t t-foreach="orders" t-as="order">
<tr>
<td>
<t t-esc="order.name"/>
</td>
<td>
<t t-esc="order.date_order"/>
</td>
<td>
<t t-esc="order.partner_id.name"/>
</td>
<td>
<t t-esc="order.state"/>
</td>
<td class="text-end">
<t t-esc="order.amount_untaxed"/>
</td>
<td class="text-end">
<t t-esc="order.amount_tax"/>
</td>
<td class="text-end">
<t t-esc="order.amount_total"/>
</td>
</tr>
</t>
</tbody>
</table>
<t t-if="not orders">
<div class="alert alert-info mt-3">
No sale orders found.
</div>
</t>
</div>
</t>
</template>
</odoo>
All of the sale orders will now be displayed on the /saleorders page, as seen in the image below.
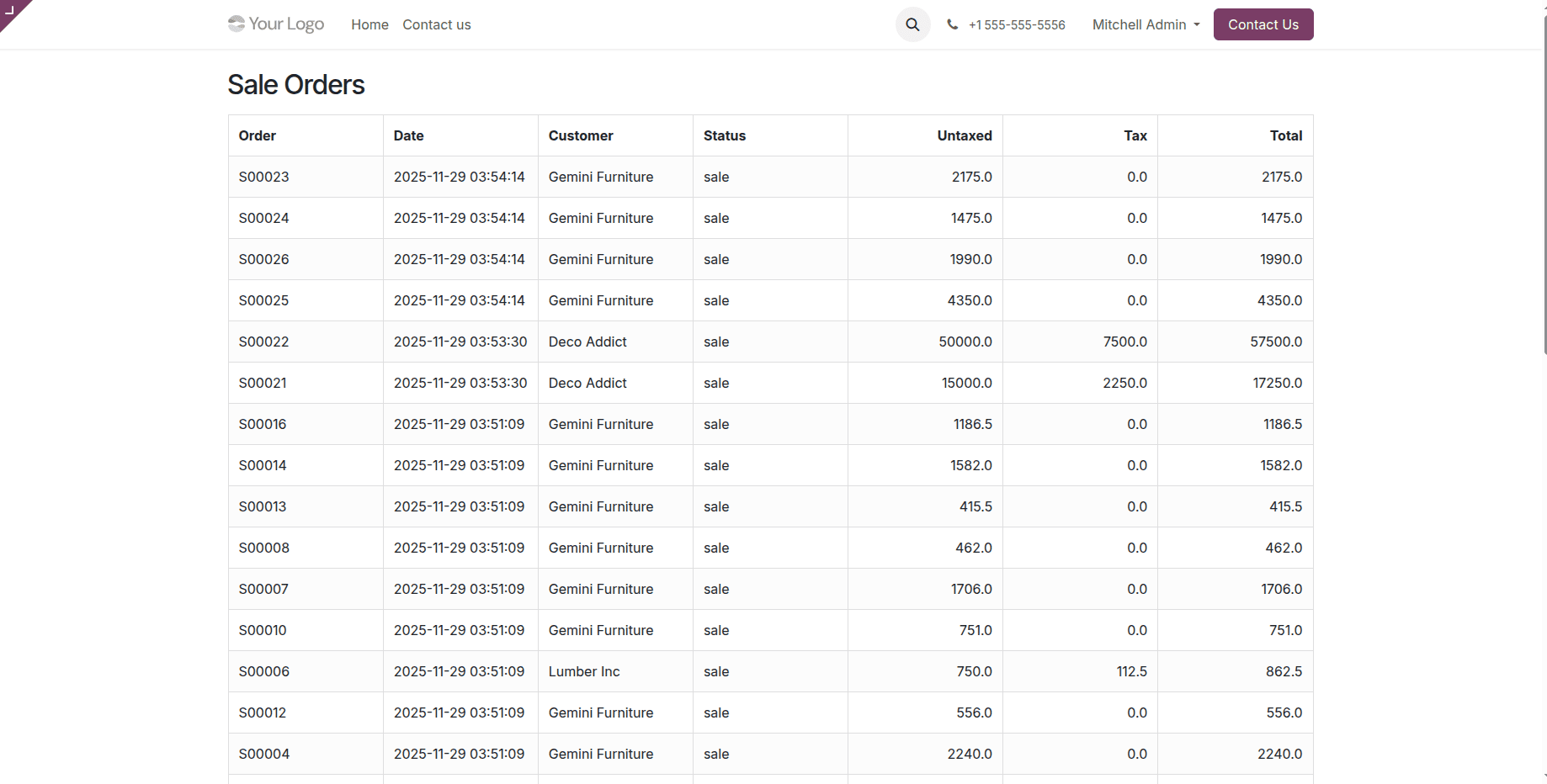
In conclusion, by specifying routes, putting business logic into practice, and managing answers, web controllers in Odoo let you personalize web interactions. These are flexible tools for creating unique online experiences in Odoo 19.
To read more about How to Create & Configure Web Controllers in Odoo 18, refer to our blog, How to Create & Configure Web Controllers in Odoo 18.